
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin E: A fat-soluble antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- Supports Health: Enhances immune function, promotes skin health, and may have cardiovascular benefits.
- Deficiency: Rare but can lead to neurological and muscular problems.
- Food Sources: Include nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, and leafy greens.
Vitamin E Overview
Vitamin E is a group of fat-soluble compounds known for their antioxidant properties. It helps protect cells from oxidative stress, which can contribute to aging and various diseases. Vitamin E exists in several forms, with alpha-tocopherol being the most biologically active.
Vitamin E Benefits
- Antioxidant Protection: Acts as an antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- Immune Support: Enhances the activity of immune cells, helping the body defend against infections and illnesses.
- Skin Health: Reduces inflammation, supports wound healing, and protects against UV damage.
- Cardiovascular Health: May have benefits such as reducing oxidative stress in blood vessels and improving cholesterol levels.
Deficiency Symptoms
Vitamin E deficiency is rare but can lead to:
- Neurological Issues: Muscle weakness, vision problems, and coordination difficulties.
- Immune Impairment: Reduced immune function and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Anemia: In severe cases, vitamin E deficiency can contribute to hemolytic anemia.
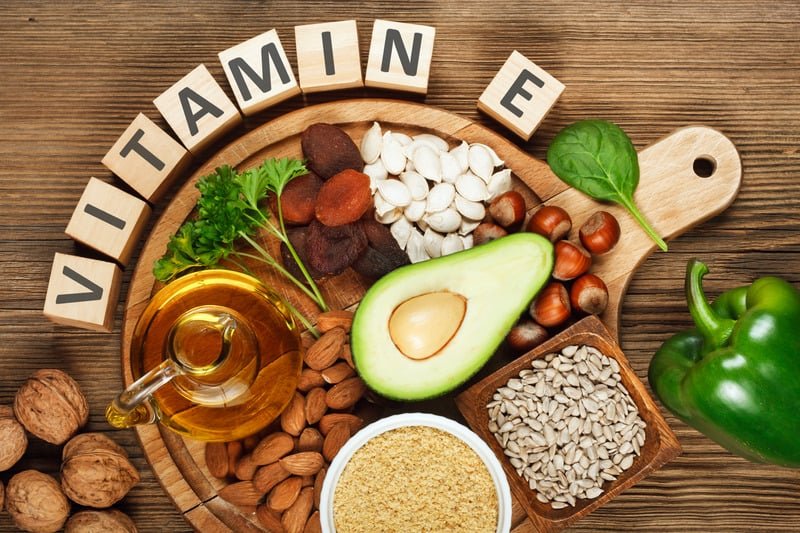

Food Sources
Good food sources of vitamin E include:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts.
- Vegetable Oils: Olive oil, sunflower oil, and wheat germ oil.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard.
- Fortified Foods: Some cereals and fruit juices are fortified with vitamin E.
How Vitamin E Works in the Body
Vitamin E functions primarily as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a role in immune function, skin health, and cardiovascular health.
How Things Go Bad
While vitamin E deficiency is uncommon, it can occur due to:
- Poor Diet: Not consuming enough vitamin E-rich foods.
- Digestive Disorders: Conditions that impair fat absorption, such as Crohn’s disease or cystic fibrosis.
- Genetic Disorders: Rare genetic conditions that affect vitamin E metabolism.
Types of Vitamin E Supplements
Vitamin E supplements are available in various forms, including:
- Alpha-Tocopherol: The most common and biologically active form of vitamin E.
- Mixed Tocopherols: Supplements that contain a mix of different vitamin E forms.
- Vitamin E Complexes: Supplements that combine vitamin E with other antioxidants or nutrients.
Dosage Recommendations
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin E varies based on age and gender:
- Adults: The RDA for adult men and women is 15 milligrams (mg) of alpha-tocopherol.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant and breastfeeding women may require slightly higher amounts, around 15-19 mg per day.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Research Studies on Vitamin E
- Antioxidant Benefits: Studies have shown that vitamin E supplementation can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in various conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
- Skin Health: Promotes skin healing, reduces UV damage, and improves overall skin health.
- Immune Function: May enhance immune cell activity and support immune responses.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Potential cardiovascular benefits, particularly in reducing oxidative damage to blood vessels, though findings have been mixed.
Vitamin E Final Thoughts
Vitamin E is an essential nutrient with antioxidant properties that support overall health and well-being. While deficiency is rare, consuming vitamin E-rich foods or supplements can contribute to optimal health, especially for immune function, skin health, and cellular protection.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this document is for educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.

Leave A Comment